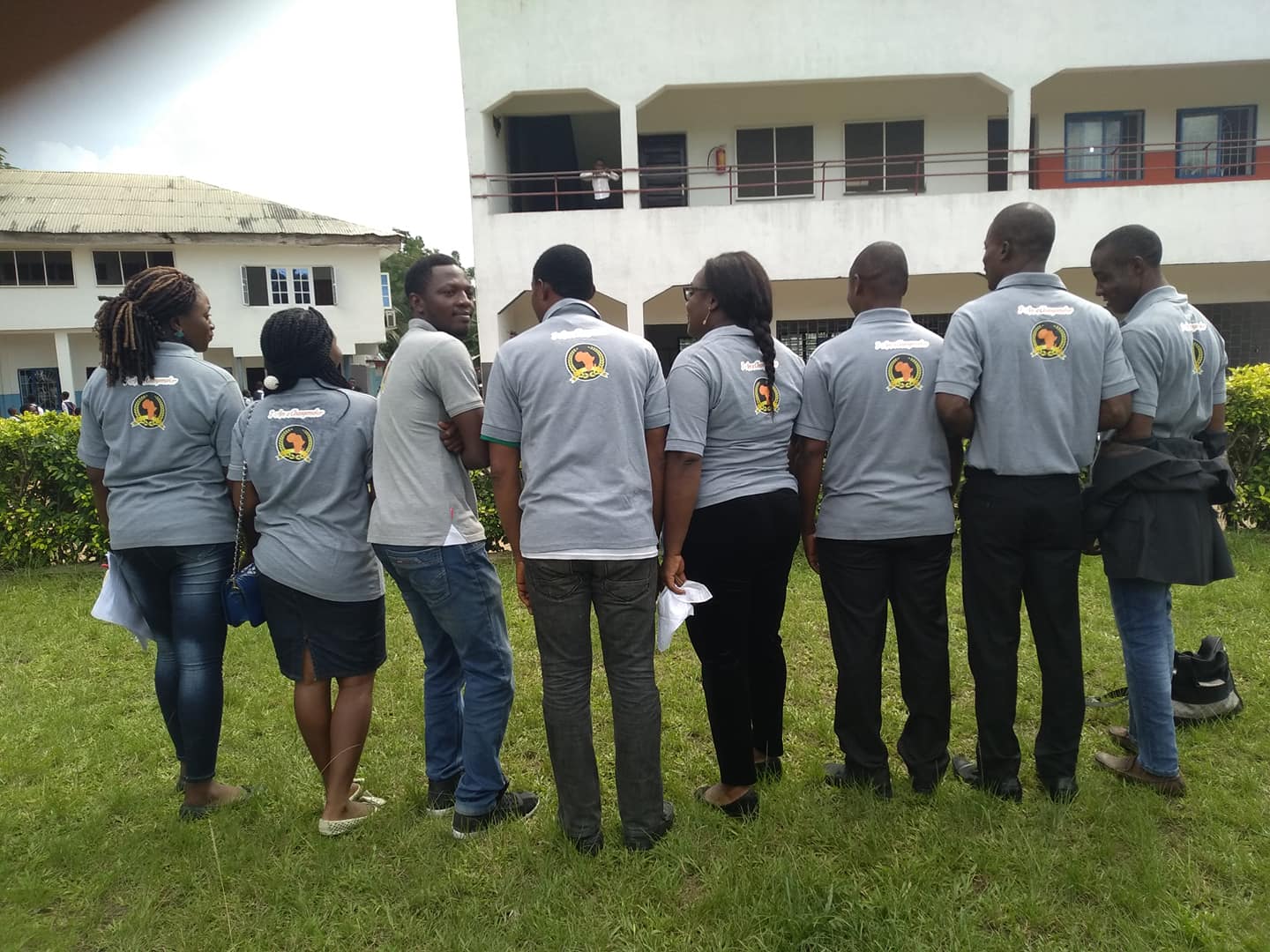
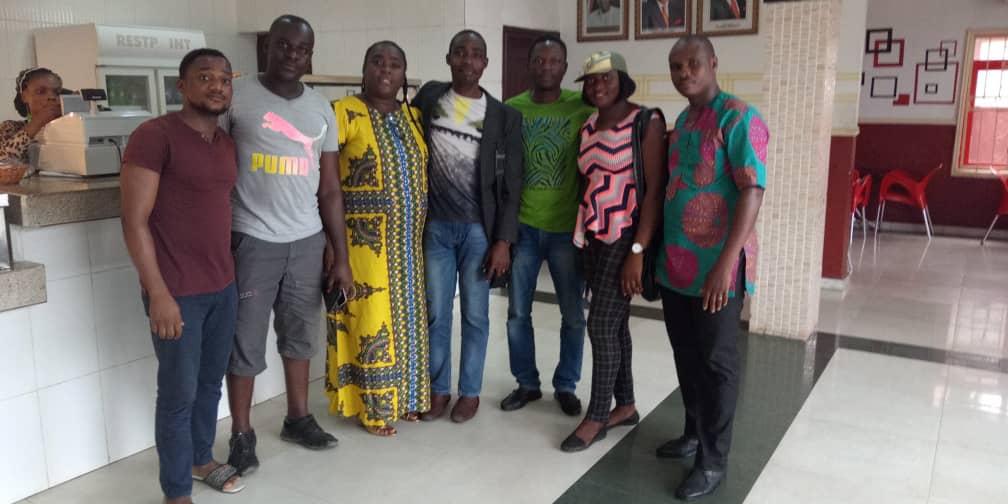
African ChangeMakers Fellows Cohort 2 ( Akwa-Ibom, Nigeria) Team Project on Youth Violence – PART 1
AFRICAN CHANGEMAKERS FELLOWS COHORT 2 (AKWA IBOM STATE – NIGERIA)
TEAM PROJECT ON YOUTH VIOLENCE – PART 1
INTRODUCTION
In the past and even in the present dispensation, violence has taken her toll on individuals and groups in the society.
The question arises: What is violence? Violence is defined as “the intentional use of physical force or power, threatened or actual, against another person or against a group that results in or has a high likelihood of resulting in injury, death, psychological harm, under development, or deprivation”.
Youth violence is violence among young people, typically children, adolescents and young adults between the age of 10 and 24. Youth violence is a global public health problem. It includes a range of acts from bullying, physical fighting, threats with weapons, gang related violence, to more sexual and physical assault to homicide. A young person can be involved with youth violence as a victim, offender and witness.

Research and programmes addressing youth violence typically include people aged 10–29 years, although patterns of youth violence can begin in early childhood. Worldwide, an estimated 200 000 homicides occur each year among youth and young adults aged 10–29 years, making homicide the fourth leading cause of death in this age group. Eighty three percent of homicide victims in this age group are male, and nearly all of these deaths occur in low and middle-income countries (WHO 2015).
Violence among youth in Nigeria has cast a dark shadow over prospect for a peaceful, united, secure and prosperous society. There has been a noticeable increase in the incidence of violent crimes and young cults in secondary schools. 42% of boys and 32% of girls in developing countries are exposed to bullying (WHO).

YOUTHS AS INSTRUMENT OF VIOLENCE
In Nigeria, youths constantly get involved in violence, probably due to their young age characterized by great physical and mental strength which can be misused due to frustration and depression. Some youths drop-out of school or do not want to learn trade, thus become idle and possible instrument of violence when not properly mentored and groomed. Some politician resort to engaging these set of youths negatively and using them as political thugs during election. A young people must be occupy in positive activities so as not to misuse his/her time, energy and resources
CAUSES OF YOUTH VIOLENCE
Media influence, Teen neighborhood, Domestic and child abuse, Insufficient parental supervision, Peer pressure, Drug use, Trauma, Mental illness, Idleness example school drop-out etc, Unemployment, Corruption, Decadence of communal values.

THE EFFECT OF YOUTHS VIOLENCE
Youth violence can have immediate and life-long physical, emotional, and economic consequences. It takes a huge toll on our young people, no matter if they are the victim, the aggressor, or a witness. And, it hurts everyone else in a community. Youth violence is a leading cause of death for adolescents and young adults. Some forms of youth violence, such as bullying, slapping, or hitting, can cause severe emotional harm, nonfatal physical injuries, and long-lasting problems. Beyond deaths and injuries, youth violence can lead to mental health problems and increased health-risk behaviors, such as smoking, alcohol and drug use, and unsafe sex. Youth violence results in greatly increased health, welfare and criminal justice costs; reduces productivity; decreases the value of property in areas where it occurs; and generally undermines the fabric of society.
In addition to causing injury and death, youth violence affects communities by increasing the cost of health care, reducing productivity, decreasing property values, and disrupting social services
When youth violence occurs, the entire community is affected. Children cannot play outside if their neighborhoods and playgrounds are unsafe. Young people cannot learn and succeed in life if they are afraid to go to school. Violence also harms families, businesses, and other parts of a community by increasing health care costs, decreasing property values, and disrupting services.
These effects can be seen in areas of social, economic, religious and cultural perspective.
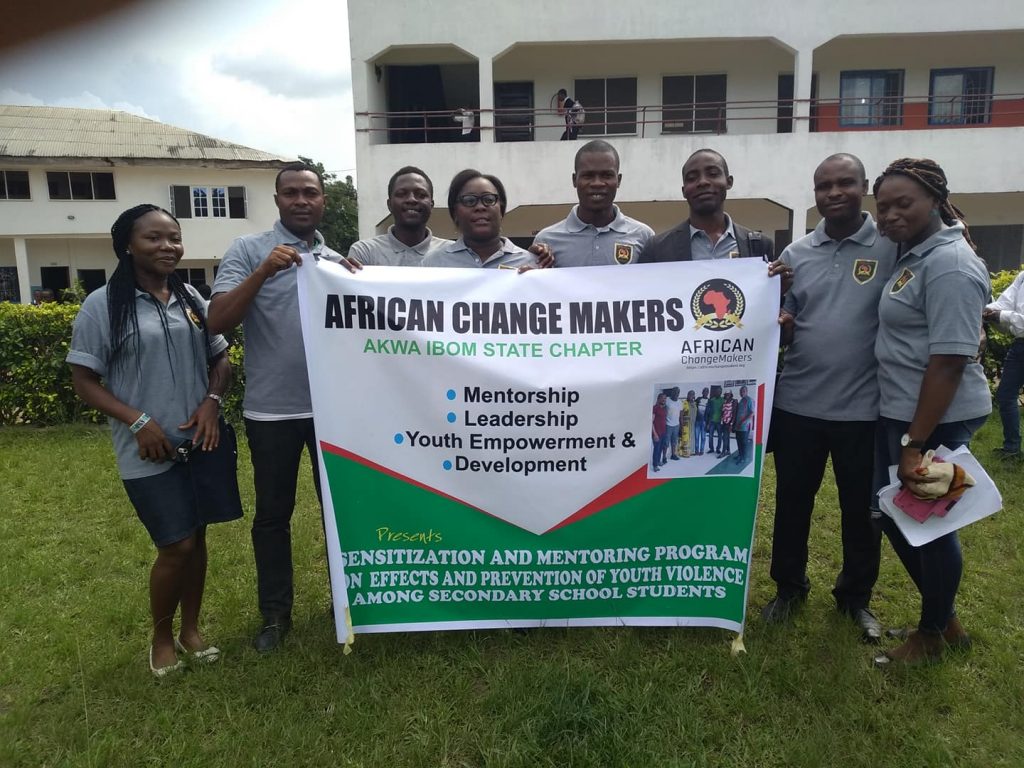

TACKLING VIOLENCE
What works best is a combination of care, punitive, educational and employment measures. The government wants to do more than simply set limits by imposing penalties on youths who have committed a crime. It is also important to offer young people the prospect of work or education. This will keep them from embarking on a life of crime.
Preventing youth violence thus requires a comprehensive approach that also addresses the social determinants of violence, such as income inequality and low levels of social protection, and which strengthens the institutional mechanisms, resources and human capacity needed to ensure the just, effective and accountable enforcement of laws.
Early intervention plays an important role in keeping minors from embarking on a life of crime. Swift and consistent punishment for offences can help reduce the incidence of crime. After serving their sentence, young offenders receive support aimed at preventing re-offending.
Accordingly, effective youth violence prevention programmes can improve a broad range of health, education and social outcomes, leading to potentially substantial economic savings. Everyone is involved in tackling youth violence, the family, society, school, churches and government.
SKILL ACQUISITION AS ONE OF THE MEAN OF TACKLING YOUTH VIOLENCE
Skill acquisition is one of the means of occupying the youth’s energy, time, resources and curbs youth violence.
Skills Acquisition is the key to reduce high level of poverty and unemployment rate in Nigeria. The contribution of Skill Acquisition and training on unemployment reduction through youth empowerment and social welfare service improvement will be much significant if encouraged at all level in the state especially at local and community level. Acquisition of vocational skills leads to a significant reduction of poverty among young adults who participated on skills acquisition programmes. Because Nigeria is fast becoming a predominantly youthful society with high rate of unemployment, it requires training the youth in entrepreneurship skills in technical vocational education and training to tackle unemployment which has reached alarming proportions. Youth unemployment remains a major challenge to the developmental process of the Nigerian economy. Youth unemployment appears to be shooting up the sky as many Nigerian youths lack appropriate skills that will empower them after graduation from school. Most youths graduate from school without the needed skills or competencies that would enable them function in today’s emerging society.
The importance of entrepreneurship skills acquisition cannot be over-emphasized since appropriate skills acquisition through entrepreneurship will help to make young school leavers to be self-reliant and boost their economic status. Entrepreneurship has been identified globally and nationally as a tool for generating a sustainable economy which is the core value of the National Economic Empowerment Development Strategies (NEEDS). Through such Skills Acquisition, the establishment of small businesses helps to generate substantial amount of employment and income which are essential parts of a country’s Gross National Product (GNP) on the one hand and reduce unemployment on the other. For the laudable benefits of entrepreneurship skills acquisition to manifest in our youths’ and the general public, skills must be learned through formal or non-formal settings. When youths are empowered through the acquisition of entrepreneurial skills, there is the possibility that they will use the skills to create new avenues for wealth. Empowering the youth to set up businesses involves proper acquisition of skills through education and training. Such acquisition opens one’s eyes to forecast business opportunities using appropriate entrepreneurship skills.

Examples of skill acquisition are: Computer skill, fashion designing, snack production, shoe making, repair and maintenance of electronic devices, dancing, online marketing etc
VIEW ALL PICTURES AT: https://flic.kr/s/aHsmuv8Bs6
By ACFellows Cohort 2 (Akwa-Ibom, Nigeria)
#ACFellowshipCohort2
#ACFellowsAkwaIbom
#AfricanChangeMakers
#iamthechangeAFRICA